1. Setting up our Bastion Host
Intro
As one of the most popular Infrastructure-as-a-service platforms, AWS is a good choice to experiment with this. Additionally, everything we're wanting to do here will fit within the bounds of AWS Free Tier.
With a few tweaks we will be able to use the AWS Systems Manager Connect to access the machine in case we accidentally lock ourselves out with SSH during our experimentation!
Setting up the lab in AWS
I'm assuming at this stage you have a free account and can login to console.aws.amazon.com, if not that's the pre-task.
Create and launch a new EC2 instance selecting the default AMI of "Amazon Linux 2", all the default settings and choosing the option to have AWS generate an ssh key-pair for you.
In IAM (Identity and Access Management) create a new IAM Role called something like "EC2 SSM Connect" with the following policy
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": "ec2.amazonaws.com"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}
]
}Then add the permission
AmazonSSMManagedEC2InstanceDefaultPolicyto this role.Assign this role to your newly created EC2 instance from step 1.
You will need to update the network access control list (NACL) for the subnet in which your EC2 instance is running to accommodate the following:
Type Protocol Ports CIDR Why? Inbound TCP 22 'YOUR IP ADDRESS' So you can connect in from your SSH client Inbound TCP 32768-609991 0.0.0.0/0 So you can complete the TCP handshake over HTTPS to the SSM Agent endpoint Outbound TCP 443 0.0.0.0/0 So you can connect to the SSM Agent endpoints (Note, best practice is actually to use a VPC endpoint, then you can allowlist a fixed IP for that, otherwise this would usually be a gaping egress hole in your NACL) Outbound TCP 32768-60999 'YOUR IP ADDRESS' So you can complete the TCP handshake with your SSH client (assuming your EC2 instance is running) wait for about 15 minutes. Why? For the SSM to connect to an instance the instance is waiting for something called the Instance MetaData Service (IMDS) API to be locally available to register with, once this is available we will be able to connect in using our browser.
To connect, you'll need to visit the following URL replacing the
{YOUR INSTANCE ID}with your id that begins ini-:
"https://console.aws.amazon.com/ec2/home?#ConnectToInstance:instanceId={YOUR INSTANCE ID}"If you haven't waited long enough (step 6) OR you haven't configured IAM correctly (step 4) then you will see this message:
We weren't able to connect to your instance. Common reasons for this include:
- SSM Agent isn't installed on the instance. You can install the agent on both Windows instances and Linux instances.
- The required IAM instance profile isn't attached to the instance. You can attach a profile using AWS Systems Manager Quick Setup.
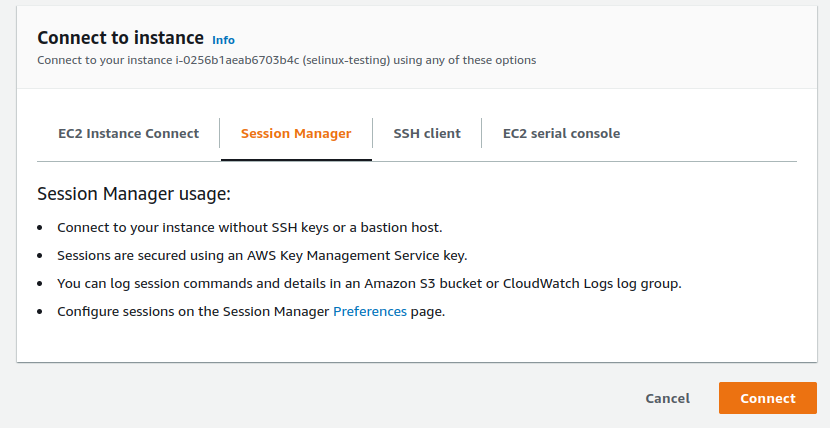
If it's ready to connect you should see the following
Once you're in you can now run a command like (order by most recently started process descending):
watch -n 1 'ss | grep -i ssh'Then when we connect over SSH in the next part of the lab we'll see something like this:
Every 1.0s: ss | grep -i ssh
tcp ESTAB 0 0 <EC2 INSTANCE IP ADDRESS>:ssh <YOUR IP ADDRESS>:39136
- The ephemeral ports can be listed on a linux host by running
$ sysctl net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range. (at time of writing) On Amazon Linux 2 this returns the range 32768-60999.↩